Understanding Multi-Agent Environments
At its core, a multi-agent environment is a dynamic ecosystem of independent yet cooperative entities, each contributing toward shared or complementary goals. To understand how these agents coordinate effectively, it helps to break down the key building blocks of such systems.
Core Components
Autonomous Agents
Each agent operates independently, guided by its specific goals and the data it has access to.
-
A data agent may fetch, clean, or transform data.
-
A reasoning agent might analyze patterns or generate insights.
-
A policy agent enforces compliance and governance rules.
Together, these specialized agents form a distributed intelligence network where decisions and actions are made locally but contribute to a global objective.
Shared Memory and Context
Effective coordination depends on a common understanding of the environment. Agents rely on a shared memory layer — such as a vector database or semantic graph — to store context, actions, and results. This prevents redundant work, reduces conflicts, and ensures every agent operates with up-to-date information.
Communication Protocols
Agents communicate using APIs, message queues, or event buses. These channels define how information flows between agents — how messages are sent, received, and acknowledged — ensuring clarity, reliability, and smooth collaboration.
Coordination Mechanisms
Schedulers and orchestrators ensure that tasks run in the right order, workloads are balanced, and dependencies are respected. They act as the backbone of synchronization, helping agents work together efficiently and avoid bottlenecks.
 Fig 2: Structure of Multi-Agent Systems
Fig 2: Structure of Multi-Agent Systems Architectural Models
-
Centralized Coordination
A single orchestrator or controller manages all agent interactions. This model offers simplicity and control, but can become a bottleneck at scale. -
Decentralized Coordination
Agents coordinate directly with each other in a peer-to-peer fashion. It’s more scalable and resilient, but also harder to monitor and govern. -
Hybrid Coordination
A balanced model that combines centralized planning with decentralized execution — allowing strategic oversight while preserving flexibility. For most enterprises, this hybrid approach delivers the best mix of scalability, control, and resilience. -
Types of Agents and Their Roles
Not all agents are created for the same purpose. In enterprise environments, agents typically fall into four main categories, each playing a distinct role within the larger AI ecosystem.
Communication, Context, and Shared Goals
Communication is not just about data exchange — it’s about shared understanding. For coordination to work, agents must operate in the same context and align with the same goals.
-
Contextual Memory
NexaStack uses a context-first approach, where all agents can access and update shared memory containing state, history, and reasoning traces. This ensures decisions are informed and non-redundant.
-
Goal Alignment
NexaStack’s goal propagation mechanism distributes a larger enterprise objective into smaller sub-goals for individual agents. As priorities evolve, each agent dynamically adjusts its actions to stay aligned.
-
Semantic Communication
NexaStack structures agent communication in machine-readable formats like JSON-LD and RDF, ensuring consistent interpretation across all agents.
Common Bottlenecks in Coordination
Even advanced systems struggle with coordination bottlenecks as they scale. Some typical ones include:
-
Latency in Communication – Delays cause agents to act on outdated information.
-
Inconsistent Context – If memory isn’t shared properly, agents lose synchronization.
-
Resource Contention – When multiple agents fight for limited compute or API bandwidth, performance drops.
-
Lack of Observability – Without clear visibility, debugging or enforcing governance becomes difficult.
Coordination Challenges in Enterprises
In enterprises, these challenges become more pronounced. Legacy systems, siloed data, and strict policies create barriers that traditional agent frameworks can’t handle efficiently.
-
Fragmented Systems and Data
Agents operating across multiple tools and data formats often lose context. NexaStack unifies this through a consistent data fabric.
-
Conflicting Objectives
Different departments may optimize for different goals. NexaStack ensures all agents align with overall business priorities.
-
Latency and Reliability
Enterprises need real-time decisions. NexaStack uses event-driven coordination and load balancing to maintain performance under pressure.
-
Security and Compliance
As agents gain autonomy, governance becomes essential. NexaStack integrates encryption, RBAC, and compliance policies at every step.

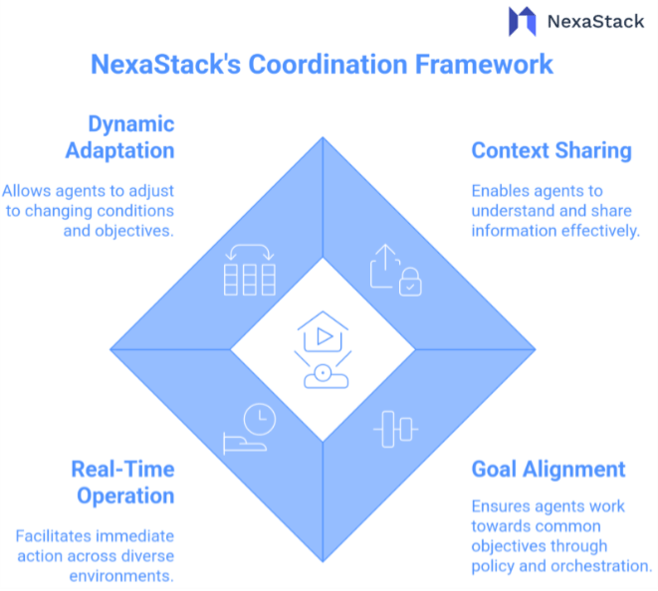
NexaStack’s Coordination Framework
NexaStack provides a context-aware coordination layer that supports both centralized and decentralized models.
Context-First Infrastructure
A distributed memory layer keeps all agents in sync with shared states and reasoning traces. Structured and unstructured data coexist to create a holistic view of the system.
Orchestration and Choreography
-
Orchestration: Centralized coordination for predictable workflows like compliance.
-
Choreography: Event-driven, decentralized coordination for adaptive systems.
NexaStack supports both — even hybrid workflows that blend the two. -
Shared Memory and Context Management: NexaStack maintains a consistent, queryable memory fabric so agents can reflect on past actions and plan future ones together.
-
Real-Time Observability: Integrated tools let teams visualize agent communication, monitor performance, detect anomalies, and receive instant alerts.
Key Enablers of Effective Coordination
Behind NexaStack’s coordination framework are several powerful architectural enablers:
-
Event-Driven Workflows
Agents respond instantly to changes, making coordination asynchronous, flexible, and scalable — perfect for use cases like incident response or dynamic customer engagement.
-
Resource-Aware Scheduling
Schedulers allocate compute and memory based on agent priorities, preventing conflicts and ensuring predictable performance.
-
Built-In Governance and Security
Role-based access, encryption, and compliance engines maintain safety, trust, and auditability across all interactions.
-
Hybrid and Legacy Integration
NexaStack connects agents across cloud-native and legacy systems, allowing end-to-end automation within existing enterprise ecosystems.
Use Cases of NexaStack in Multi-Agent Coordination
NexaStack’s coordination capabilities come to life through real-world applications.
- Customer Service Automation
-
Task agents handle queries and responses.
-
Coordinator agents manage escalation and routing.
-
Observer agents monitor performance and sentiment.
-
Policy agents enforce privacy and compliance. The result is faster, more personalized support with consistent quality.
- IT and Security Operations
-
Security agents detect anomalies.
-
Remediation agents act automatically.
-
Coordinator agents orchestrate workflows.
-
Policy agents ensure compliance. This creates a self-healing IT ecosystem that responds in real time.
-
Data Engineering and Analytics
-
Task agents manage ETL and validation.
-
Coordinate agents' schedules and optimize pipelines.
-
Observer agents ensure data quality.
-
Policy agents uphold governance.
NexaStack ensures reliability and transparency across the data lifecycle.
- Industry-Specific Applications
NexaStack adapts seamlessly across industries:
-
Manufacturing – predictive maintenance and IoT monitoring
-
Finance – fraud detection and regulatory reporting
-
Healthcare – automated patient workflows
-
Retail – demand forecasting and personalized experiences
Each case benefits from the same principle: intelligent coordination at scale.
The Future of Multi-Agent Coordination
As enterprises evolve toward self-optimizing AI systems, NexaStack lays the foundation for the next leap — truly autonomous coordination.
-
Self-Organizing and Self-Healing Agents
Agents will soon be able to reorganize, rebalance workloads, and recover from errors without manual intervention — guided by NexaStack’s decentralized frameworks.
-
Cross-Domain Collaboration
NexaStack allows agents from different domains — HR, finance, IT — to share context and collaborate toward enterprise-wide goals, breaking long-standing silos.
-
The Path Toward Autonomous Enterprises
In the future, enterprises won’t just automate tasks — they’ll automate decision-making itself. NexaStack is paving the way for this transformation by providing the underlying intelligence, observability, and governance needed for true autonomy.
Conclusion
NexaStack’s Strategic Role
NexaStack isn’t just another infrastructure layer — it’s the coordination engine behind modern multi-agent AI systems. It enables independent agents to share context, communicate effectively, and act in sync, transforming isolated automation into a unified, intelligent network.
By managing interactions, data exchange, and decision flows, NexaStack helps organizations build systems that are faster, smarter, and more resilient. It eliminates the chaos of disconnected AI tools, providing a cohesive foundation where every agent contributes to a larger, coordinated purpose.
Roadmap for Enterprises
Enterprises aiming to embrace this new era of agentic AI should:
-
Build shared context layers to enable consistent collaboration among agents.
-
Adopt event-driven coordination for real-time adaptability and responsiveness.
-
Reinforce governance and observability to maintain transparency and trust.
-
Leverage platforms like NexaStack that simplify multi-agent orchestration at scale.
By turning automation into collaboration and intelligence into coordination, NexaStack empowers organizations to move beyond traditional AI workflows — toward a future of truly autonomous, self-managing enterprises.