Key Drivers Behind RLaaS Adoption
Organizations are turning to Reinforcement Learning as a Service (RLaaS) because they need systems that don’t just analyze data — they must learn continuously and make better decisions over time. Below are the main reasons driving this shift:
-
The Need for Adaptive Intelligence: Traditional ML follows a train → deploy → retrain cycle, which works only when environments are stable. When markets shift or user behavior changes, performance drops. RLaaS allows models to learn continuously from real-time feedback, so strategies improve without constant manual retraining
-
Complex Decision-Making Requirements: In many real-world scenarios, the challenge is not just predicting what will happen, but deciding what to do next.
This applies to:
-
Robotics, where machines must decide how to move safely and efficiently.
-
Operations and resource planning, where decisions today shape costs tomorrow.
-
Financial trading, where each action influencing long-term outcomes and risk exposure.
RLaaS focuses on learning policies — long-term strategies — rather than one-off predictions. This makes it ideal for systems where actions and outcomes are interconnected.
-
Safe and Scalable Training Through Simulation: Training in the real world can be expensive, slow, or risky. For example:
-
A self-driving car cannot “learn by crashing.”
-
A medical dosage recommendation system cannot “learn by making mistakes.”
-
A warehouse robot cannot “learn by causing operational downtime.”
RLaaS platforms often include built-in simulation environments that allow agents to experiment safely. This makes it possible to train large-scale, high-stakes decision systems without real-world consequences, accelerating development while reducing risk.
-
Real-Time Personalization: Unlike static recommendation engines, reinforcement learning systems can tailor strategies based on ongoing behavior — not just historical patterns.
This enables applications such as:
-
Personalized e-learning platforms that adapt difficulty based on student performance
-
Gaming environments that respond to player style and skill progression
-
Recommendation engines that adjust suggestions as user interests evolve
By continuously incorporating feedback, RLaaS supports dynamic and context-aware personalization, making experiences feel more intuitive and responsive.
Shifts from Traditional MLaaS to Reinforcement Learning
Traditional MLaaS relies on supervised or unsupervised models trained on historical data. These models are deployed with fixed behavior, and when real-world conditions change, they need to be retrained. This works well for stable environments, but it falls short in situations that evolve.
Reinforcement Learning takes a different approach. Instead of learning only from past data, RL systems improve through interaction and feedback. The model takes an action, sees the result, and adjusts its strategy to maximize long-term outcomes.
This represents a meaningful shift in how AI systems are built and deployed:
-
From fixed models → to adaptive learning systems
-
From static predictions → to dynamic, ongoing strategy optimization
-
From achieving accuracy on past data → to continually improving performance in changing environments
In essence, the move from MLaaS to RLaaS is a shift from asking “What is likely to happen?” to asking “What is the best decision to make, now and over time?”
This enables AI systems to behave more like autonomous decision-makers, learning and refining their actions as the world evolves — rather than remaining tied to what was true during training.
Understanding Traditional MLaaS
MLaaS platforms provide end-to-end tools for building, training, deploying, and managing machine learning models. They simplify the development lifecycle by offering cloud infrastructure and automated components.
Core Features and Services
MLaaS platforms typically include:
-
Pre-built algorithms for classification, regression, clustering, and forecasting tasks
-
Data preprocessing and feature engineering tools to clean and transform raw data
-
Distributed training environments that help scale model training efficiently using cloud computing
-
Managed model serving and API hosting, making deployment straightforward
-
Monitoring and observability dashboards to track accuracy, drift, latency, and performance
Strengths for Enterprises
MLaaS works well in environments where the patterns in data are relatively stable. Key advantages include:
-
Faster development and deployment, enabling rapid prototyping to production
-
Broad applicability across industries like finance, healthcare, retail, and marketing
-
Lower skill requirements, making machine learning accessible to teams without deep AI expertise
-
Cost effectiveness when models don’t require constant retraining or adaptation
Limitations for Enterprises
However, MLaaS also has constraints that become noticeable in dynamic or real-time environments:
-
Static behavior — models remain fixed after deployment and only improve through retraining.
-
Inability to model sequential decision-making, where current actions influence future outcomes.

What is RLaaS?
Reinforcement Learning as a Service provides cloud-based infrastructure and tools to develop agents that learn by interacting with environments. RLaaS platforms supply computational resources, training engines, simulation environments, and policy evaluation frameworks.
Key Capabilities
-
Continuous learning from real or simulated experience
-
Policy optimization that focuses on long-term strategy rather than one-time predictions
-
Simulation-driven experimentation, enabling safe and cost-effective learning
-
Automated balancing between exploring new actions and exploiting known best actions
This model is suited for applications where conditions change, feedback is available, and decisions create cascading effects. 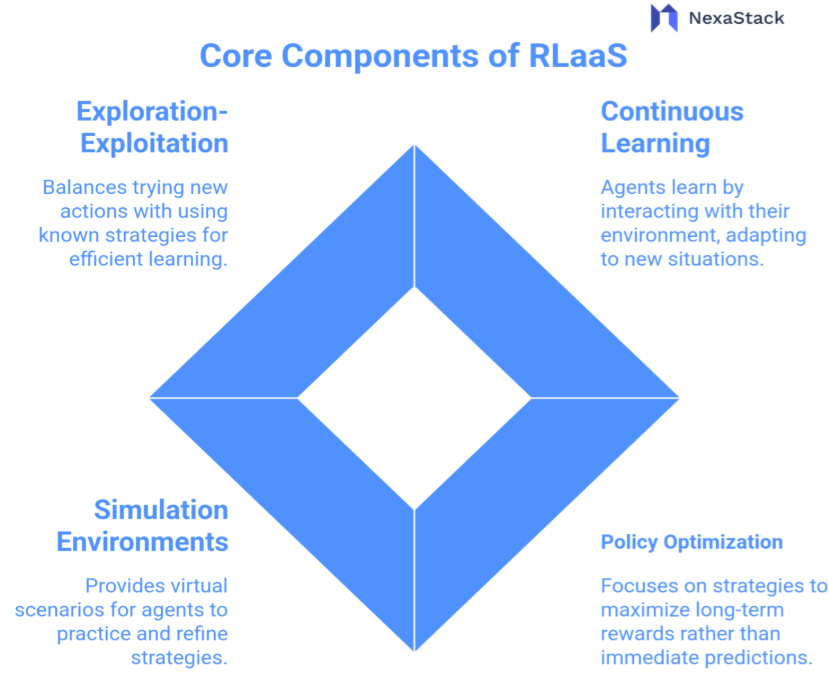
Key Differences: RLaaS vs Traditional MLaaS
The core difference between RLaaS and MLaaS lies in how they learn and how they respond to change. MLaaS is focused on making predictions from historical data, while RLaaS focuses on learning the best actions through trial, feedback, and continuous improvement.
|
Feature |
Traditional MLaaS |
RLaaS |
|
Data Requirements |
Labelled datasets |
Simulated or real-time interaction data |
|
Training Approach |
Batch learning |
Online learning |
|
Model Adaptability |
Static |
Adaptive and evolving |
|
Deployment |
Predictive APIs |
Decision-making agents |
|
Scalability |
Scales with data volume |
Scales with environmental complexity |
|
Cost Considerations |
Lower for simple tasks |
Higher due to compute-intensive training |
Advantages of RLaaS for AI Teams
-
Continuous Learning and Improvement
RLaaS removes the need for repeated manual retraining. The system learns from ongoing interaction, refining its strategy automatically as conditions change. -
Strong Performance in Changing Environments
When markets, operations, or user behaviors shift, RL agents adapt in real time. Traditional ML models tend to degrade unless retrained, while RLaaS keeps improving. -
Real-Time Decision-Making
RLaaS is built for systems that must act, not just predict.
This makes it well-suited for robotics, automated control systems, logistics optimization, and dynamic resource allocation, where fast, context-aware decisions are essential.
When to Choose Traditional MLaaS
MLaaS remains the best fit in scenarios where the goal is accurate prediction rather than ongoing decision-making.
Choose MLaaS when:
-
The Task Is Predictive and Static
Use it for fraud detection, churn prediction, credit scoring, and similar use cases where patterns are well-understood, and outcomes don’t depend on continuous interaction. -
Faster Deployment Is Important
MLaaS platforms offer ready-made tools and infrastructure, helping teams move quickly from prototype to production. -
The Environment Is Stable
If conditions change slowly, periodic retraining is enough. In these cases, MLaaS is simpler and more cost-efficient than implementing reinforcement learning.
Comparative Use Cases
RLaaS and MLaaS are suited to different types of problems. The choice depends on whether the system needs to predict outcomes or continuously adapt decisions.
Where RLaaS Performs Best
RLaaS is ideal for environments that change frequently and require real-time action.
-
Robotics & Autonomous Systems – Learning how to move, navigate, and adjust to surroundings.
-
Supply Chain Optimization – Adapting routing and allocation based on shifting demand and resource constraints.
-
Real-Time Personalization – Updating recommendations or experiences as user behavior evolves.
-
Gaming and Simulations – Learning strategies that improve through interaction.
-
Autonomous Finance – Optimizing long-term trading and portfolio strategies based on ongoing market feedback.
Where MLaaS Remains Ideal
MLaaS works best when the task is predictive, and patterns are relatively stable.
-
Fraud Detection and Risk Scoring
-
Demand and Sales Forecasting
-
Customer Segmentation and Behavior Analysis
-
Language and Document Classification
Challenges and Considerations
Integration Complexity
RL systems require environments—either real-time or simulated—where agents can interact and learn. Creating these environments can require engineering investment.
Talent and Skill Requirements
Successful RL adoption involves expertise in:
-
Reward and incentive design
-
Algorithm and policy tuning
-
Stability and performance management at scale
Security, Compliance, and Data Governance
Because RL often learns from live operational data, centralized monitoring and guardrails are essential to avoid unintended behavior.
Building the Right Strategy
-
Evaluate Business Needs and Maturity
Adopt RLaaS only when:
-
Decisions are sequential and interdependent
-
The environment is dynamic
-
Real-time feedback is available
-
Teams can manage an iterative improvement cycle
-
Consider Hybrid Models
Many enterprise architectures combine ML and RL:
-
ML models generate predictions (e.g., demand forecast)
-
RL agents take actions based on these predictions (e.g., production scheduling)
-
Roadmap for Adoption
- Identify suitable adaptive decision-focused use cases
- Develop or integrate a simulation or real-time environment
- Train RL agents and validate performance
- Deploy with monitoring and safety guardrails
- Continuously refine policies based on outcomes
Conclusion
Choosing between MLaaS and RLaaS is not about determining which is universally superior. The best approach depends on the nature of the problem:
-
MLaaS is optimal for static, prediction-driven tasks where cost efficiency and rapid deployment matter.
-
RLaaS is ideal for dynamic, interactive, decision-driven systems that require continuous learning and optimization.
The future of enterprise AI is increasingly hybrid—combining predictive models for insights with reinforcement learning agents for strategic action. As organizations mature in their AI capabilities, RLaaS will play a critical role in enabling intelligent, autonomous systems that move beyond prediction to continuous strategic improvement.