What Are AI Fact Sheets?
AI Fact Sheets complement Model Cards by serving as comprehensive compliance dashboards for AI systems. They document a model’s legal, ethical, and operational adherence, helping organizations maintain transparency, accountability, and trustworthiness throughout the model’s lifecycle. Fact Sheets go beyond technical metrics—they also provide insight into risks, governance practices, and operational readiness.
Core Components:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Demonstrates that AI models adhere to relevant laws and standards, such as GDPR, the EU AI Act, and NIST AI RMF.
Example: A hiring AI system is designed to avoid gender-based discrimination, ensuring compliance with employment regulations.
-
Risk Assessment & Mitigation: Identifies potential issues such as biases, security vulnerabilities, or operational risks, and describes the safeguards in place.
Example: An autonomous delivery drone includes a manual override to prevent accidents in case of system failure, protecting both people and property.
-
Version Control & Audit Trails: Tracks updates to models, documenting what changes were made, why, and by whom. This enables full traceability for audits, regulatory reviews, and internal governance.
-
Operational Readiness: Provides detailed information about deployment requirements, system performance, scalability, and latency, ensuring the model can operate reliably in real-world environments.
Why They Matter:
-
For Lawyers & Auditors: Fact Sheets serve as verifiable evidence of compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
-
For Business Leaders: Ensure that AI initiatives align with organizational ethics, governance policies, and risk management strategies.
-
For Incident Response Teams: Provide a clear record of model changes, allowing rapid investigation and remediation if issues arise.
 Fig 3: AI Fact Sheet Components
Fig 3: AI Fact Sheet Components
Governance Across the Inference Lifecycle
AI governance is not a one-time task—it must cover the entire lifecycle of a model, from development to ongoing use. Effective oversight ensures models remain accurate, fair, and compliant as they interact with real-world data.
-
Pre-Deployment: Before a model goes live, it should undergo bias audits to detect unfair treatment of any group and performance benchmarking to confirm it meets required accuracy and reliability standards.
-
Runtime Monitoring: Once deployed, models need continuous monitoring. Drift detection identifies shifts in input data that could affect performance, while anomaly logging flags unexpected predictions or behaviors that might indicate errors or emerging risks.
-
Post-Inference Review: After the model produces results, it’s important to evaluate its real-world impact and integrate feedback. This might include updating datasets, refining training, or adjusting decision-making rules to improve fairness and effectiveness.
Key Insight:
Model Cards and AI Fact Sheets should evolve alongside the model, documenting behavioral changes over time. Continuous updates ensure transparency and support ongoing governance, making AI systems more auditable and trustworthy.
 Fig 4: AI Inference Lifecycle and Governance
Fig 4: AI Inference Lifecycle and Governance Model Metadata: The Backbone of Transparency
Structured metadata answers critical governance questions:
|
Category |
Key Details |
|
Training Data |
Sources, preprocessing, biases |
|
Model Architecture |
Framework, parameters |
|
Performance Metrics |
Accuracy, F1-score, fairness indices |
|
Risk Disclosures |
Known failure modes, adversarial vulnerabilities |
Best Practices:
-
Use standardized metadata schemas such as MLflow or Datasheets for Datasets to ensure consistency across models.
-
Include fairness evaluations, such as the Disparate Impact Ratio, to monitor and mitigate potential bias.
-
Keep metadata up to date with model retraining and version updates to maintain accuracy and governance compliance.
Eval Hooks: Continuous Assessment
Static documentation alone cannot ensure AI remains trustworthy over time. Eval Hooks are automated mechanisms that continuously monitor, evaluate, and safeguard models throughout their lifecycle.
What They Do:
-
Fairness Checks: Monitor prediction outcomes to detect disparities across demographic or user groups, ensuring the model treats all groups equitably.
-
Drift Detection: Identify shifts in data distribution or input patterns that could degrade model performance over time.
-
Adversarial Robustness Testing: Evaluate the model’s resistance to manipulative inputs or attacks that could produce incorrect or biased outputs.
Implementation:
-
Pre-Deployment: Run unit tests to verify that the model meets defined thresholds for accuracy, fairness, and safety before release.
-
Production: Use real-time dashboards to continuously track model performance, alerting teams if anomalies or drifts occur.
-
Post-Hoc Audits: Generate automated compliance and evaluation reports to document performance, risk mitigation, and any updates applied to the model.
By integrating Eval Hooks, organizations can proactively detect issues, maintain fairness, and ensure regulatory compliance, rather than relying solely on periodic manual reviews.
Best Practices for Governance-Ready Artifacts
-
Standardize Templates for Consistency
Using consistent templates ensures that every Model Card or AI Fact Sheet captures the same critical information. This makes it easier for stakeholders—developers, auditors, or regulators—to compare models and spot gaps quickly. Open-source frameworks or internal style guides can help maintain uniformity. -
Balance Technical and Non-Technical Details
Governance documents should be understandable for both technical teams and non-technical stakeholders. Include clear explanations of model behavior, risks, and limitations alongside technical metrics, so everyone from executives to auditors can grasp the key insights. -
Automate Updates with Retraining
AI models evolve, and so should their documentation. Automating updates ensures that metadata, performance metrics, and risk disclosures remain current whenever a model is retrained or updated. This reduces manual effort and improves reliability for audits and compliance checks. -
Align with Regulations (GDPR, EU AI Act, NIST AI RMF)
Compliance isn’t optional. Ensure your artifacts explicitly address regulatory requirements, like explainability under GDPR, risk mitigation for high-risk AI under the EU AI Act, or best practices outlined in NIST AI RMF. This alignment strengthens legal defensibility and promotes responsible AI deployment.
Conclusion
Model Cards and AI Fact Sheets are not just static documentation—they are key enablers of AI governance. By systematically addressing the full spectrum of responsible AI practices, organizations can ensure their models are transparent, accountable, and reliable.
-
Inference Lifecycle Monitoring: Continuously track model behavior during deployment, detect anomalies, and assess real-world impact to maintain performance and fairness over time.
-
Model Metadata Transparency: Provide clear, structured information about training data, architecture, performance metrics, and known risks, giving stakeholders confidence in model decisions.
-
Eval Hooks and Continuous Checks: Automate fairness, robustness, and drift evaluations to proactively detect and mitigate potential issues throughout a model’s lifecycle.
By integrating these practices, organizations can create auditable and trustworthy AI systems that are aligned with legal, ethical, and operational standards. Establishing Model Cards and AI Fact Sheets as a standard part of the AI development process is essential for fostering responsible AI that users, regulators, and society can trust.
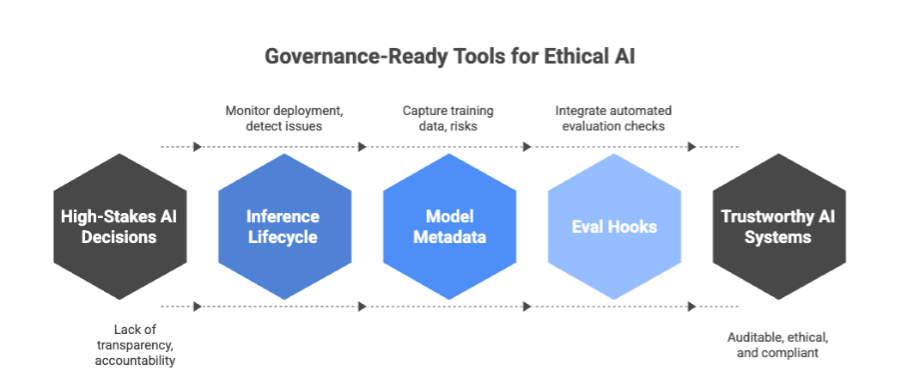
 Fig 2: Model card Components
Fig 2: Model card Components 




