Alignment with Global Frameworks (EU AI Act, NIST AI RMF, ISO 42001)
Organizations must align with emerging global frameworks and standards—both to manage risk and build trust.
EU AI Act
The EU AI Act categorizes AI systems by risk levels and mandates obligations (e.g., transparency, human oversight, documentation). For agentic systems, this is especially relevant because their autonomy can fall into “high-risk” categories.
NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF)
The NIST framework offers a flexible, voluntary structure for assessing, mitigating, and monitoring AI risks, encompassing governance, explainability, fairness, and robustness. Enterprises are increasingly referencing it as a blueprint for success.
ISO 42001 (Hypothetical/Future standard)
While ISO 42001 (AI Management Systems) is still in development, it signals that international standards for AI governance, management, and operations are forthcoming. Aligning early with standards-based controls—and integrating Agentic GRC workflows—gives organizations a head start.
How Agentic GRC Supports Alignment
-
Documentation and versioning modules help meet regulatory documentation obligations (e.g., EU AI Act Article 11) for high-risk systems.
-
Risk management workflows within GRC align directly with NIST phases (e.g., Govern, Map, Measure, Manage, Monitor).
-
Audit trails, agent action logs, and model lineage support standard compliance and certification readiness.
-
Continuous monitoring tools built into Agentic GRC help maintain compliance over time, not just at the time of deployment.
By embedding these frameworks into your governance architecture, you proactively meet regulatory demands, build stakeholder trust, and reduce the risk of non-compliance.
Embedding a Governance-Culture for Agentic Systems
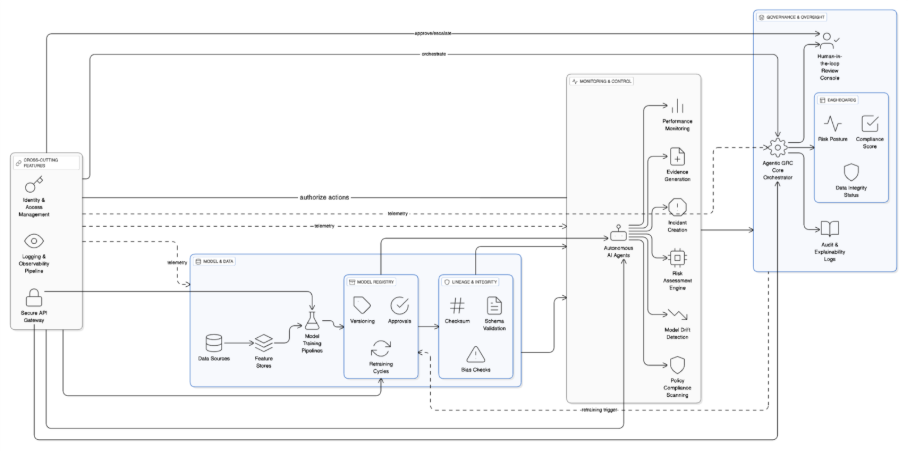
Governance isn’t a dashboard or a compliance checklist—it’s a living culture. For organizations deploying agentic AI, true responsibility begins when governance is woven into everyday decisions, team behavior, and technology workflows. This is where Nexastack’s integrated approach makes the difference: by embedding governance and monitoring directly into AI operations, it ensures that responsible practices are not optional—they’re operational.
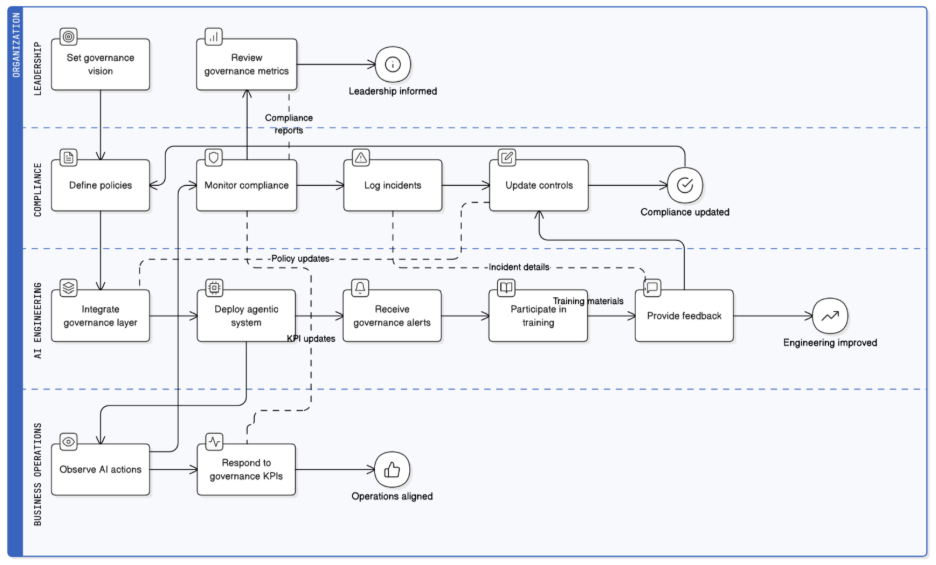
Leadership & Ownership
Accountability must start at the top. Boards, compliance heads, and AI engineering teams require shared visibility into how autonomous systems behave and learn. With Nexastack’s unified observability layer, executives can view governance metrics—model compliance scores, bias alerts, data lineage—in a single pane of glass. This clarity turns governance from an afterthought into a leadership-level KPI.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
AI governance spans data science, security, legal, risk, and business operations. Nexastack enables cross-team orchestration through policy-driven workflows—so when one agent acts autonomously, its actions are logged, verified, and shared across compliance and technical teams in real time. This breaks silos and ensures that governance keeps pace with agility.
Training & Awareness
Agentic AI introduces new risks, including prompt injection, emergent behaviors, and unexplainable reasoning. Nexastack supports in-context governance alerts and guided training for developers and operators, ensuring that human oversight remains aware of model intent and risk. Every AI action becomes a teachable moment for continuous improvement.
Incentives & Metrics
Governance succeeds when it’s measurable. Nexastack embeds governance KPIs—such as trust index, model drift rate, and compliance adherence—into operational dashboards. Teams can see their governance score in the same way they view uptime or latency. This alignment encourages proactive governance behavior and rewards responsible engineering.
Continuous Improvement
AI evolves—and so must governance. With Nexastack’s audit intelligence and feedback loops, every incident or model deviation feeds back into policy refinement. Post-incident retrospectives automatically generate governance insights and recommended control updates. This transforms compliance into a self-learning system that evolves in tandem with the AI itself.
By fostering a governance-first mindset and enabling it through Nexastack’s platform, organizations align people, processes, and technology—creating a culture where AI acts responsibly by design, not by enforcement.
Continuous Monitoring and Model Validation
AI governance doesn’t end when a model goes live—it begins there. For agentic systems, where decisions and adaptations occur autonomously, continuous monitoring and validation are crucial for maintaining control, trust, and compliance. Nexastack makes this ongoing vigilance practical and automated.
Real-Time Operational Monitoring
Nexastack’s real-time observability engine tracks every model and agent activity—inputs, outputs, reasoning chains, performance metrics, tool invocations, and fairness indicators. Drift detectors and anomaly monitors send alerts into the governance dashboard, enabling teams to act before an issue escalates. Instead of reactive governance, organizations gain predictive control.
Model Validation & Retraining
Governance must span the entire model lifecycle. With Nexastack’s integrated validation pipelines, organizations can run pre-deployment fairness and bias tests, as well as trigger post-deployment drift checks, automatically. When a model crosses compliance thresholds, Nexastack can initiate governance workflows—from retraining requests to rollback or decommissioning—without human delay.
Audit & Reporting
Compliance audits shouldn’t be an exercise in data gathering. Nexastack automates governance reporting, generating structured documentation that includes model cards, risk summaries, lineage diagrams, and incident logs. These reports align with global frameworks, such as the EU AI Act, NIST AI RMF, and ISO 42001, providing organizations with audit readiness through minimal manual effort.
Feedback & Governance Loops
When an AI system behaves unexpectedly, Nexastack’s closed-loop governance engine captures the incident, analyzes root causes, updates policies, and retrains relevant models. Each governance loop strengthens the overall system—turning incidents into institutional learning.
From Ethical AI to Autonomous AI Governance
As organizations evolve from deploying AI models to managing autonomous, agentic systems, the governance challenge grows just as rapidly. Principles such as transparency, fairness, and accountability are essential—but they must be implemented beyond policy statements into operational practice.
With Nexastack at the core of Agentic GRC, governance becomes a living system: cultural in spirit, technical in execution, and measurable in impact. Organizations not only meet compliance requirements but also build trustworthy, self-regulated AI ecosystems where innovation and responsibility advance hand in hand.