AI Governance and Compliance Frameworks
Automating compliance through policy-as-code ensures regulatory adherence without slowing AI development. Frameworks like Open Policy Agent (OPA) and Kubernetes-native tools (Kyverno) embed governance rules directly into deployment pipelines, allowing real-time adjustments as laws evolve. AI models must also maintain detailed audit logs, recording decisions with cryptographic signatures to support transparency and accountability.
Explainability is another critical requirement. Techniques like SHAP (Shapley Additive exPlanations) and LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) help make AI decisions understandable to regulators and end-users. National AI registries can track high-risk systems, while automated monitoring tools detect model drift and generate compliance reports for oversight bodies.

Architectural Models for Sovereign AI Private Clouds
|
Model |
Description |
Example Use Cases |
|
Fully On-Premise National AI Data Centres |
Government-controlled AI infrastructure |
Military AI, national healthcare systems |
|
Hybrid Sovereign Cloud Models |
Mix of private and regulated public clouds |
Smart cities, financial AI |
|
Federated Sovereign AI Architectures |
Cross-institutional AI collaboration with shared governance |
Research consortia, pan-European AI initiatives |
Benefits of Sovereign AI Platforms with National Oversight
Governed by national authorities, sovereign AI platforms offer significant advantages in today's geopolitically complex digital landscape. Countries can achieve greater security, compliance, and strategic autonomy by controlling AI infrastructure, data, and governance. Below, we explore the key benefits in detail.
- Enhanced Data Privacy & Security
Minimises Exposure to Foreign Surveillance & Cyber Threats
Sovereign AI platforms ensure that sensitive data—from citizen records to defence intelligence—remains within national borders and is processed under strict government oversight. This reduces risks such as:
-
Foreign Surveillance: Prevents unauthorised access by foreign governments or corporations through extraterritorial laws (e.g., U.S. CLOUD Act, China’s Data Security Law).
-
Supply Chain Attacks: Mitigate risks from compromised hardware/software dependencies (e.g., backdoors in foreign-manufactured AI chips).
-
Cyber Espionage: Limits vulnerabilities from shared global cloud infrastructures (e.g., attacks on multinational cloud providers).
How It Works:
-
Data Localisation Mandates: Critical data never leaves sovereign infrastructure.
-
Zero-Trust Architectures: Every access request is authenticated and encrypted.
-
National Cryptographic Standards: Uses government-approved encryption (e.g., India’s "Indigenous Stack," EU’s post-quantum cryptography initiatives).
- Regulatory Compliance by Design
Built-In Adherence to National AI Laws
Sovereign AI platforms are engineered to comply with local AI regulations from the ground up, avoiding costly retrofits or legal conflicts. Key advantages include:
-
Automated Legal Alignment: "Policy-as-code" embeds regulations (e.g., EU AI Act, U.S. AI Executive Order) directly into AI workflows.
-
Real-Time Auditing: Immutable logs track data usage and model decisions for regulators.
-
Ethical AI Enforcement: Bans prohibited AI uses (e.g., social scoring, discriminatory algorithms) at the infrastructure level.
How It Works:
-
Pre-Approved AI Model Zoos: Governments curate compliant AI models (e.g., Germany’s "AI Testing Fields").
-
Dynamic Compliance Adjustments: Systems auto-update when laws change (e.g., new transparency rules).
- Strategic Control Over AI Capabilities
Ensures AI Development Aligns with National Interests
By retaining sovereignty over AI infrastructure, countries can:
-
Prioritise Domestic AI Innovation: Fund local startups/research (e.g., India’s "AI for All" strategy).
-
Customise AI for National Needs: Develop culturally/linguistically tailored models (e.g., Japan’s "Fugaku-LLM" for the Japanese language).
-
Secure Critical Sectors: Shield defence, energy, and telecom AI from foreign influence.
How It Works:
-
National AI Sandboxes: Testbeds for strategic applications (e.g., Singapore’s "AI Verify").
-
Sovereign AI Chips: Reduce reliance on NVIDIA/AMD (e.g., China’s Ascend, EU’s RISC-V efforts).
-
Talent Retention: Incentivises local AI experts to work on national priorities.
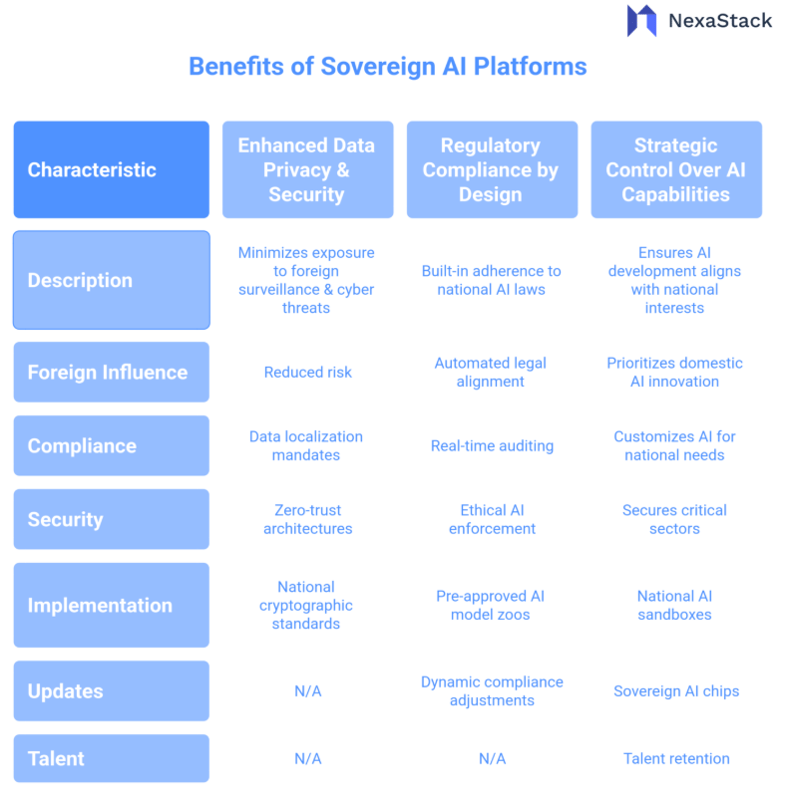 Fig 4: Benefits of Sovereign AI Platforms
Fig 4: Benefits of Sovereign AI Platforms Best Practices for Building and Managing Sovereign AI Private Clouds
Governments and enterprises must adopt rigorous operational practices to ensure sovereign AI clouds remain secure, interoperable, and compliant. Below is a detailed breakdown of the three core best practices:
- Establish Strong Governance & Policy-as-Code
Why It Matters
AI governance ensures ethical, legal, and secure AI deployment. Traditional manual compliance is slow and error-prone—policy-as-code automates enforcement.
Key Strategies
Embed Ethics & Compliance into AI Workflows
-
Define rules (e.g., "No facial recognition without consent") as machine-readable policies.
-
Use tools like Open Policy Agent (OPA) or AWS/Azure Policy-as-Code to enforce them.
Automate Regulatory Compliance
-
Map national AI laws (e.g., EU AI Act, U.S. AI Executive Order) to code.
-
Example: Auto-block AI models that don’t meet explainability requirements.
Centralised AI Governance Frameworks
-
National AI registries track high-risk models (e.g., healthcare, defence).
-
Singapore’s AI Verify provides a governance toolkit for audits.
- Leverage Open Standards for Interoperability
Why It Matters
Proprietary tech creates vendor lock-in, making sovereign clouds dependent on foreign providers. Open standards ensure flexibility and sovereignty.
Key Strategies
Adopt Open-Source AI Frameworks
-
Use PyTorch, TensorFlow, or Hugging Face instead of closed alternatives.
-
Ensures models can run anywhere, avoiding proprietary restrictions.
Standardise Data & Model Formats
-
ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange) for cross-framework compatibility.
-
Apache Arrow for efficient data interchange.
Use Sovereign Cloud Interoperability Protocols
-
GAIA-X (EU) ensures European clouds work seamlessly together.
-
India’s Aadhaar ecosystem uses open APIs to manage its identity securely.
- Implement Continuous Security & Compliance Monitoring
Why It Matters
AI systems evolve rapidly, so static security checks are insufficient. Real-time monitoring prevents breaches, bias, and regulatory violations.
Key Strategies
Real-Time AI Model Auditing
-
Track data lineage (where training data came from).
-
Monitor model drift (unexpected behaviour changes).
Anomaly & Threat Detection
-
Use AI-powered SIEM (Security Information & Event Management) tools.
-
Detect adversarial attacks (e.g., data poisoning, model evasion).
Automated Compliance Reporting
- Generate audit logs for regulators automatically.
- Flag violations (e.g., unauthorised data access) in real time.

Conclusion
Sovereign AI platforms have transitioned from technological luxury to a national security necessity. As AI becomes the defining battleground for economic competitiveness and geopolitical influence, nations must establish independent, secure, and regulated AI ecosystems.
By deploying private AI clouds with national oversight, countries can achieve three critical objectives:
-
Data Sovereignty – Ensuring sensitive information remains within borders, protected from foreign surveillance or exploitation.
-
Regulated Innovation – Cultivating homegrown AI talent and industries while maintaining ethical and legal compliance.
-
Geopolitical Resilience – Reducing dependency on foreign cloud providers and mitigating risks of sanctions or supply chain disruptions.
The global AI race is not just about technological superiority—it’s about who controls the infrastructure, data, and governance frameworks. Nations that invest in sovereign AI today will shape the rules of tomorrow’s digital economy, while those that delay risk ceding strategic autonomy to external powers.
The choice is clear: Build sovereign AI capabilities now or remain dependent on others later. The future belongs to nations that take control of their AI destiny.
 Fig 1: Foundations of AI Sovereignty
Fig 1: Foundations of AI Sovereignty 



