The Need to Evaluate and Compare Deployment Techniques
Deploying LLMs on-prem is not just about setting up infrastructure. Enterprises must weigh different techniques in terms of performance, scalability, compliance, and resource utilization. A structured evaluation ensures:
-
Optimal use of GPU/TPU resources.
-
Compliance with internal governance and audit policies.
-
Better ROI by matching techniques with business objectives.
This makes it critical to understand how prompt engineering, retrieval-augmented generation, fine-tuning, and quantization perform under enterprise constraints.
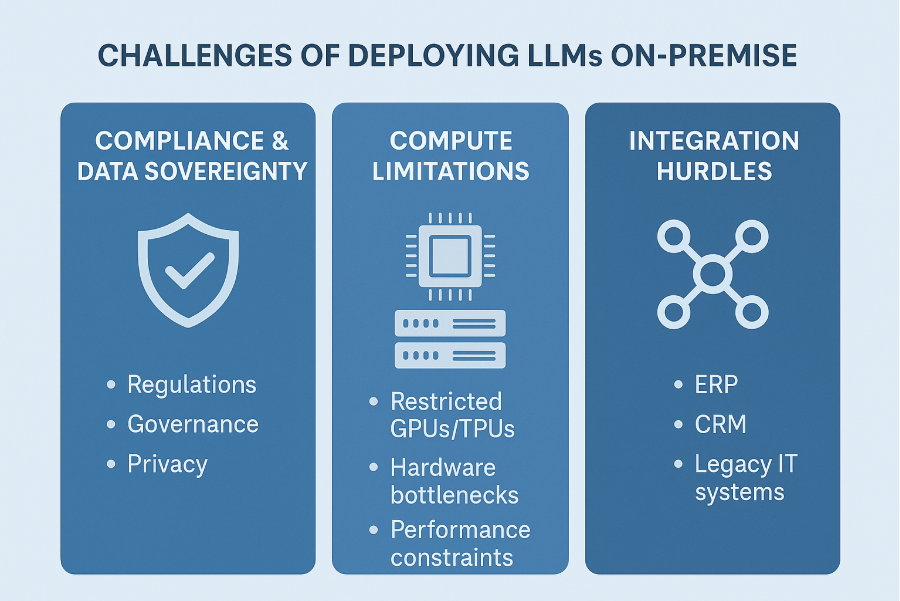
Challenges of On-Premise LLM Deployments
-
Data Sovereignty and Compliance Requirements
Ensuring that models and data comply with local and industry-specific regulations is one of the biggest challenges. For instance, European firms must comply with GDPR, while healthcare organizations in the US must comply with HIPAA.
-
Infrastructure and Compute Constraints
On-prem deployments often face limited GPU/TPU capacity. Unlike cloud providers who can scale elastically, enterprises must carefully balance compute resources with workload demands.
-
Integration with Enterprise Systems
Most enterprises operate in heterogeneous IT environments. Integrating LLMs with legacy ERP, CRM, and data warehouses adds complexity and often requires middleware or APIs for smooth workflows.
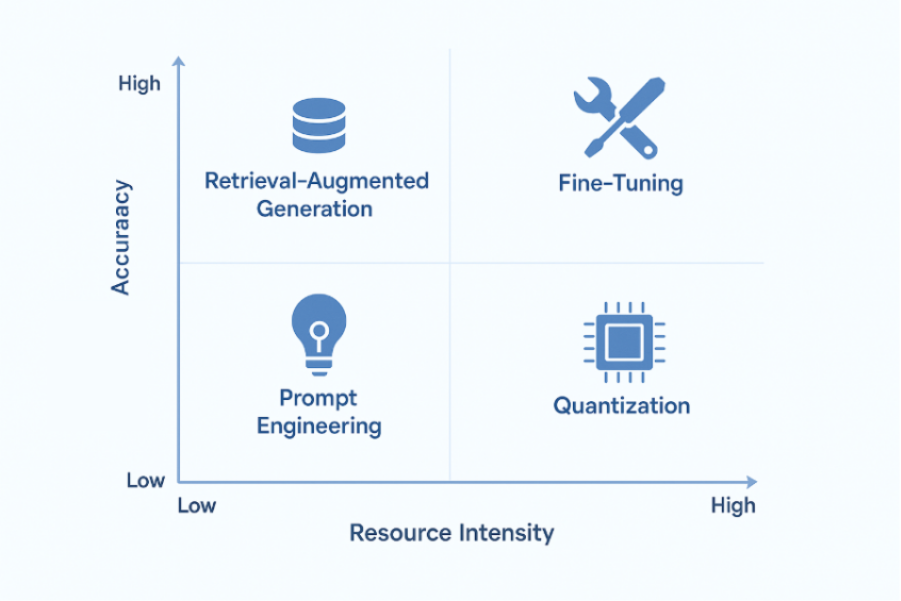
Key LLM Techniques for On-Premises Settings
Prompt Engineering and Optimization
The simplest and most resource-efficient technique. Well-designed prompts can significantly improve model output without requiring retraining.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG enhances model outputs by pulling relevant information from enterprise knowledge bases. This reduces hallucinations and ensures factual accuracy.
Fine-Tuning (Full and Parameter-Efficient Methods)
-
Full Fine-Tuning: Requires extensive compute resources but delivers maximum domain alignment.
-
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT): Techniques like LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) allow enterprises to adapt models without retraining the entire LLM.
Instruction Tuning and Domain Adaptation
Instruction tuning aligns the model with enterprise-specific workflows, ensuring outputs are context-aware.
Quantization and Model Compression
By reducing precision (e.g., FP16 or INT8), quantization makes large models run efficiently on limited hardware while maintaining acceptable accuracy.
On-Prem Considerations for Each Technique
Prompt Engineering
Lightweight optimization applied at inference time without modifying model weights, ideal for improving output quality when base domain understanding is already sufficient.
-
Works entirely at inference, no retraining pipelines
-
Emphasis on structured prompts, precise instruction framing, and few-shot examples
-
Ensure token efficiency and context-window management to minimize GPU load
-
Use prompt versioning and internal approval to support audit traceability
-
Useful when compliance requires no alterations to underlying model artifacts
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Grounds model outputs in internal enterprise data by retrieving relevant documents, improving factual accuracy without touching original model weights.
-
Requires internal vector stores (PGVector, Milvus, Chroma)
-
Secure embedding pipelines and ingestion policies for documents
-
Index refresh cycles replace full retraining during policy or content updates
-
Controls via ACLs, metadata tagging, and relevance filtering
-
Accuracy depends on document quality, chunking logic, and retrieval window design
Full Fine-Tuning
Rewrites core model weights to encode domain logic, regulatory rules, and specialized interpretation, delivering maximum precision at the cost of higher compute and governance needs.
-
Requires multi-GPU training capacity and distributed training setups
-
Strict governance, overweight changes, dataset lineage, and model registries
-
Needs drift monitoring, rollback checkpoints, and reproducible builds
-
Encodes business logic in the model, so approval cycles mirror production release
-
Highest accuracy, but also the most resource- and compliance-intensive method
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT)
Achieves domain alignment using small adapter layers instead of retraining the full model, reducing GPU cost and simplifying lifecycle management.
-
Uses LoRA, adapters, and prefix tuning to store learnable parameters
-
Keeps base weights immutable for audit and compliance review
-
Enables multiple tuned personas under one shared base model
-
Minimal compute requirement, fast iterations, and smaller artifacts
-
Adapters tracked in artifact repositories and promoted via CI/CD
Instruction Tuning
Trains the model to follow internal procedures, approval chains, document templates, and policy language so outputs mirror enterprise standards.
-
Requires curated datasets built from SOPs, classifications, workflows, and compliance rules
-
Ensures consistent response format, tone, and structure
-
Evaluation based on policy adherence rather than general accuracy alone
-
Often paired with procedural validators, style constraints, or policy checks
-
Critical when outputs must satisfy internal control and documentation standards
Quantization and Model Compression
Optimizes model footprint and inference performance by reducing precision, enabling deployment on constrained on-prem hardware with acceptable accuracy impact.
-
Uses INT8/FP8 precision to shrink memory footprint
-
Improves latency and throughput on limited on-prem GPU nodes
-
Often paired with batching, kernel optimizations, or graph simplification
-
Ideal for agents, high-volume assistants, and automation pipelines
-
Full-precision variants still recommended for risk-heavy inference
Technique-Level Comparison and Selection Criteria
Selecting the right optimization method depends on four core factors: the available compute capacity, the depth of domain reasoning required, the sensitivity of data and regulatory exposure, and the long-term maintainability of the deployment. Each technique offers distinct strengths and fits different enterprise maturity levels.
|
Technique |
GPU Impact |
Domain Accuracy
|
Compliance Strength |
Best Fit
|
|
Prompt Engineering |
Very Low |
Medium |
Low |
Lightweight optimization
|
|
RAG
|
Low-Medium
|
High |
High |
Document-grounded responses
|
|
Full Fine-Tuning |
High |
Very High |
Medium
|
Deep domain reasoning |
|
PEFT
|
Low-Medium |
High
|
High
|
Multiple domain variants
|
|
Instruction Tuning
|
Low
|
High
|
High
|
Workflow and procedural alignment
|
|
Quantization
|
Very Low
|
Low-Medium |
Medium
|
Hardware-constrained inference
|
In most on-prem environments, the strongest outcomes come from combining multiple methods depending on workload requirements, regulatory constraints, hardware limits, and the depth of domain reasoning needed. As a practical guide, the points below offer clear defaults for when each approach fits best:
-
Use prompt engineering for quick alignment without modifying model weights.
-
Choose RAG when factual accuracy relies on enterprise documents and vetted internal knowledge.
-
Apply PEFT to achieve meaningful domain tuning with minimal compute overhead.
-
Reserve full fine-tuning for high-risk or heavily regulated decision systems that require deep, rule-consistent reasoning.
-
Rely on quantization when inference speed and hardware efficiency outweigh marginal accuracy loss.
-
Use instruction tuning when outputs must adhere to internal policies, templates, and procedural standards.
Evaluation Framework for On-Prem LLM Techniques
On-prem deployments come with limits that cloud environments abstract away: fixed GPU capacity, strict data residency, audit controls, and predictable TCO. Evaluating techniques under these conditions requires clarity across four dimensions: accuracy, performance, compliance alignment, and cost. Each method behaves differently when tested against these constraints.
Accuracy and Domain Reliability
Techniques must be compared based on how reliably they produce correct, domain-aligned results using internal datasets.
-
Prompt Engineering improves output clarity but stops short of capturing deeply specialized knowledge.
-
RAG strengthens factual grounding by drawing from vetted content, making it ideal where correctness depends on internal sources.
-
Fine-Tuning and PEFT directly encode domain logic into model behaviour, delivering higher reliability where complex reasoning or compliance interpretation is required.
Evaluation recommendation: test all techniques against enterprise text corpora, process flows, and subject-matter review, not generic benchmarks.
Latency, Throughput, and Performance
Each method impacts how efficiently the model runs within fixed on-prem compute limits.
-
Quantized models offer clear advantages for latency, concurrency, and GPU utilization.
-
Prompt Engineering and RAG add minimal computational pressure.
-
Full Fine-Tuning increases inference memory requirements due to modified weight structures.
Benchmark technique choices under load: peak traffic, batch runs, burst scenarios, and multi-tenant usage.
Security, Privacy, and Compliance Alignment
On-prem evaluation must include data handling, governance visibility, and auditability.
-
RAG requires controlled access to document stores, ensuring embeddings and retrieval layers stay inside enterprise boundaries.
-
Fine-Tuning and PEFT demand strict governance over trained artifacts, weight changes, dataset lineage, and access to adapter files.
-
Instruction Tuning is strongly suited to environments with mandated format, policy adherence, or traceable logic flows.
Recommendation: evaluate techniques against real regulatory controls (GDPR, HIPAA, internal audit policies) instead of generic security checklists.
Cost and Resource Consumption
Technique choice directly impacts operational cost, training cycles, artifact storage, licensing, and GPU allocation.
-
Full Fine-Tuning drives the highest cost footprint.
-
PEFT offers substantial accuracy gains while minimizing GPU hours and storage.
-
Prompt Engineering and RAG defer most costs to inference, not retraining.
-
Quantization reduces hardware expansion needs and unlocks higher throughput on existing GPUs.
Key comparison: balance the long-term cost of iterative tuning vs. the operational savings of lightweight optimization.
Comparing Techniques for On-Premises Deployments
When evaluating techniques, enterprises must consider trade-offs:
-
Performance vs. Resource Efficiency: Full fine-tuning delivers high accuracy but requires significant compute. Quantization offers efficiency but at a potential cost to precision.
-
Scalability: RAG and instruction tuning are more scalable for enterprise-wide use cases compared to full fine-tuning.
-
Maintainability: Parameter-efficient methods simplify lifecycle management.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
On-prem LLMs deliver secure, high-performance AI where sensitive data, regulatory controls, and operational integrity require full local ownership. Adoption spans multiple sectors.
-
Finance: On-prem models enable secure document analysis, compliance checks against frameworks such as Basel III and GDPR, and fraud insights derived from transaction patterns, all without exposing internal records.
-
Manufacturing: Enterprises protect design and operational IP while using models for predictive maintenance, knowledge retrieval from technical manuals, and the generation of guided workflow instructions.
Future of On-Prem LLM Techniques
On-prem LLM adoption is moving toward systems that are continuously optimized, policy-aware, and capable of operating autonomously within enterprise boundaries.
-
Adaptive Optimization with RLaaS: Reinforcement-based tuning will allow models to adjust parameters dynamically based on usage feedback, improve accuracy for specific internal tasks, and experiment safely without exposing data outside the network.
-
Multi-Agent Orchestration: On-prem agent ecosystems will divide work across specialized models for extraction, risk assessment, compliance checks, and workflow automation. Because they operate entirely inside enterprise infrastructure, sensitive data remains protected.
-
Toward Autonomous Enterprise AI: These systems will learn from changing processes, anticipate risks or compliance impacts, execute internal tasks with minimal supervision, and embed governance controls directly into model behaviour.
Conclusion
On-premises deployment of LLMs is no longer a fringe choice; it is becoming the strategic backbone for enterprises prioritizing security, compliance, and customization. CIOs and AI leaders must weigh techniques such as RAG, fine-tuning, and quantization against performance and resource constraints. The future lies in hybrid strategies, adaptive optimization, and multi-agent orchestration that empower enterprises to fully harness AI within their controlled environments.
By following the evaluation framework and best practices outlined in this guide, organizations can build a resilient, scalable, and compliant on-prem LLM strategy—ensuring they remain competitive in the AI-driven enterprise landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
FAQs on RLaaS vs Traditional MLaaS.
How is RLaaS different from MLaaS?
RLaaS learns from rewards; MLaaS learns from static datasets.
When is RLaaS preferred?
In dynamic, real-time environments that need adaptive behavior.
Does RLaaS require more compute?
Yes — it involves continuous experimentation and simulation.
What is the main advantage of RLaaS?
It enables autonomous, continuously improving decision-making.





